![]()
 "Fifty million people in the United States have it, including
more than half the population between the ages of 60 and 74. Ninety-nine
percent of people who have it show no symptoms. Twenty percent of the
people who have it don’t know it. And everyone who has it can develop
heart disease, stroke or kidney failure as a result." William B. White,
M.D.
"Fifty million people in the United States have it, including
more than half the population between the ages of 60 and 74. Ninety-nine
percent of people who have it show no symptoms. Twenty percent of the
people who have it don’t know it. And everyone who has it can develop
heart disease, stroke or kidney failure as a result." William B. White,
M.D.
Blood pressure is measured because it is important to know the patient’s physical condition while under medical care, and it is one of the most non-invasive methods of getting an overall picture of one’s health.
Buildings are dynamic – ever changing, much like people. In the same way that monitoring blood pressure can give indications to problems or potential problems in people, measuring building pressures can give indication of a “building’s health” condition. These pressure differentials are relatively small, but over time these small pressures can have either beneficial or detrimental affects on the building, it’s contents and even it’s occupants.
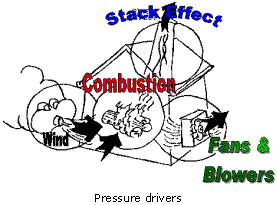 Pressures are created by one or more forces that interact with
the building. Two are of natural causes – wind and stack and two related
to human interaction - combustion and fans. There are four pressure fields
that can be measured and monitored in buildings.
Pressures are created by one or more forces that interact with
the building. Two are of natural causes – wind and stack and two related
to human interaction - combustion and fans. There are four pressure fields
that can be measured and monitored in buildings.
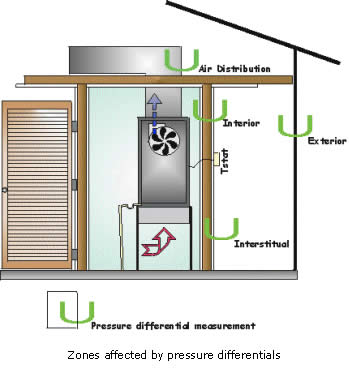
Exterior – the pressure difference across the building’s envelope as a result of natural effects such as wind and stack.
Interior – these are the room to room and room to outside differentials that can be associated with air handler fan operation, makeup air, exhaust fans, interior door closure, duct leakage, etc..
Air distribution systems – the duct work that moves air from room to room and room to outside. These “tubes” will either be at a higher or lower pressure than that of its surroundings so that air can be moved from place to place
Interstitial – there are cavities within the building that act as "ducts". Generally, these cavities are not considered to have air movement or pressure differentials, but in fact may have large pressure differentials and move a great deal of air.